Japanese sake YAMATO SHIZUKU JUNMAI GINJO
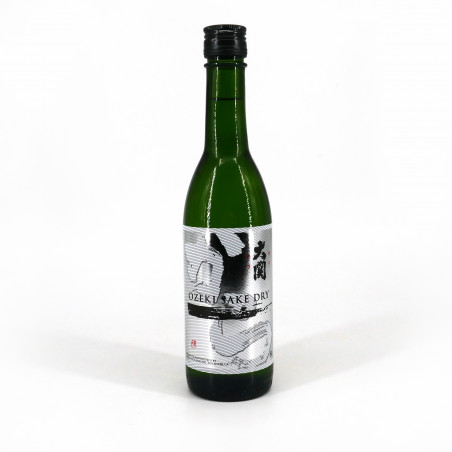
Japanese Sake OZEKI KARATANBA HONJOZO NAMACHOZOSHU alc.15.5% 300ML

Alcohol abuse is bad for your health, please consume in moderation
Delivery times :
- 1 to 3 working days for France, Belgium and Switzerland.
- 3 to 5 working days for other countries in Europe
- 3 to 5 working days for other countries via DHL
This item is shipped from our warehouse in France.
You may return or exchange an item within 14 days of receiving your order. For more information, see our Return Policy
| Capacity | 300 ml |
|---|---|
| Product origin | made in Japan |
| Production region | Kobe - Hyogo Prefecture |
| Sake family | Honjozo |
| Alcohol | 15.5% |
| Nihonshudo | +5 |
| Acidity | 1.4 |
| Polishing | 70 |
| Rice | Yamadanishiki |
Japanese Sake OZEKI KARATANBA HONJOZO NAMACHOZOSHU alc.15.5% 300ML
There are four main types of sake.
- Ginjo style sake: Sake with fruity and floral aromas, with low acidity and relatively mild. More than 60% of the rice used in their composition has been polished.
- Junmaï-style sake: rich and dense sake with cereal notes and a more pronounced acidity. The addition of alcohol is not allowed. It is a sake made from 100% fermented rice.
- Honjozo style sake: Dry and easy to drink, with a higher acidity. The addition of distilled alcohol at the end of fermentation is allowed.
- Daïginjo-style sake: These are the top-of-the-range Japanese sake with absolute refinement and complex flavours. More than 50% of the rice used in their composition has been polished.
The polishing rate corresponds to the percentage of the grain of rice that is retained. The outer husk contains lipids, vitamins and proteins, and it is important to reduce them as they degrade the aromas. The heart of the rice grain is rich in starch giving it a light and fresh taste.
Nihonshudo, literally nihonshu sake and do degree, is a scale that measures the density of sake, determined by the fermentation process of rice, in relation to the density of water. A positive value indicates that the sake is dry, while a negative value indicates a sweeter sake.
It is yeast (Kōji) that breaks down the starch in rice into alcohol and sugar. The remaining sugar determines the average density of the beverage. A large residual sugar content gives sake a negative nihonshudo.
Nigori-type sake has a Nihonshudo of -10, whereas light, dry sake has a Nihonshudo of more than 16% alcohol with low residual sugar levels.
A sake as dense as water will therefore have a nihonshudo of 0 (considered neutral).